|
|
|
|
#1 |
|
|
A paper published today in Geophysical Research Letters finds that sea surface temperatures [SSTs] in the Southern Okinawa Trough off the coast of China were warmer than the present during the Minoan Warm Period 2700 years ago, the Roman Warm Period 2000 years ago, and the Sui-Tang dynasty Warm Period 1400 years ago. According to the authors, "Despite an increase since 1850 AD, the mean [sea surface temperature] in the 20th century is still within the range of natural variability during the past 2700 years."
In addition, the paper shows the rate of warming in the Minoan, Roman, Medieval, and Sui-Tang dynasty warm periods was much faster than in the current warming period since the Little Ice Age. The paper finds "A close correlation of SST in Southern Okinawa Trough with air temperature in East China, intensity of East Asian monsoon and the El-Niño Southern Oscillation index has been attributed to the fluctuations in solar output and oceanic-atmospheric circulation 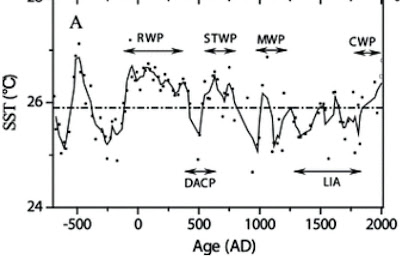 econstructed Sea Surface Temperatures [SSTs] over the past 2700 years. The Minoan, Roman {RWP], & Sui-Tang dynasty [STWP] warm periods were all warmer than the current warm period [CWP]. The Dark Ages Cold Period [DACP] and Little Ice Age [LIA] are also shown Geophysical Research Letters Sea surface temperature variability in southern Okinawa Trough during last 2700 years Weichao Wu, Wenbing Tan, Liping Zhou, Huan Yang, Yunping Xu http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/201...GL052749.shtml Most of the temperature reconstructions for the past two millennia are based on proxy data from various sites on land. Here we present a bidecadal resolution record of sea surface temperature (SST) in Southern Okinawa Trough for the past ca. 2700 years by analyzing tetraether lipids of planktonic archaea in the ODP Hole 1202B, a site under the strong influence of Kuroshio Current and East Asian monsoon. The reconstructed SST anomalies generally coincided with previously reported late Holocene climate events, including the Roman Warm Period, Sui-Tang dynasty Warm Period, Medieval Warm Period, Current Warm Period, Dark Age Cold Period and Little Ice Age. However, the Medieval Warm Period usually thought to be a historical analogue for the Current Warm Period has a mean SST of 0.6–0.8°C lower than that of the Roman Warm Period and Sui-Tang dynasty Warm Period. Despite an increase since 1850 AD, the mean SST in the 20th century is still within the range of natural variability during the past 2700 years. A close correlation of SST in Southern Okinawa Trough with air temperature in East China, intensity of East Asian monsoon and the El-Niño Southern Oscillation index has been attributed to the fluctuations insolar output and oceanic-atmospheric circulation. |
|
|
«
Previous Thread
|
Next Thread
»
| Currently Active Users Viewing This Thread: 1 (0 members and 1 guests) | |
|
|







 Threaded Mode
Threaded Mode
